What is OPC and OPC UA?
OPC facilitates communication flow between devices and systems from different vendors. But what sets apart the classic OPC standard from OPC UA (Unified Architecture)?

The initial OPC standard debuted in 1996, highlighting a pressing necessity for an open solution to enable communication between equipment and systems from diverse vendors. This led to swift adoption by both hardware and software providers, propelling OPC to industry standard status within just two years. Following this success, the OPC Foundation emerged as a non-profit organization tasked with developing and maintaining OPC, thus spearheading advancements in this communication platform.
Classic OPC standards
To begin with, OPC standards relied on Microsoft technology and constrained to Windows operating systems. OPC, an acronym for OLE (Object Linking and Embedding) for Process Control, facilitated the distribution of data between software components using COM/DCOM.
The OPC DA (Data Access) was the first OPC standard to enter the market. Early in the 2000s, several other OPC standards became available: OPC A&E (Alarm & Events), OPC HDA (Historical Data Access), OPC XML/CSV, and OPC DX (Data Exchange). In some cases, an OPC server may have multiple of these standards implemented. OPC DA is still the most widespread standard and used in many factories and facilities.
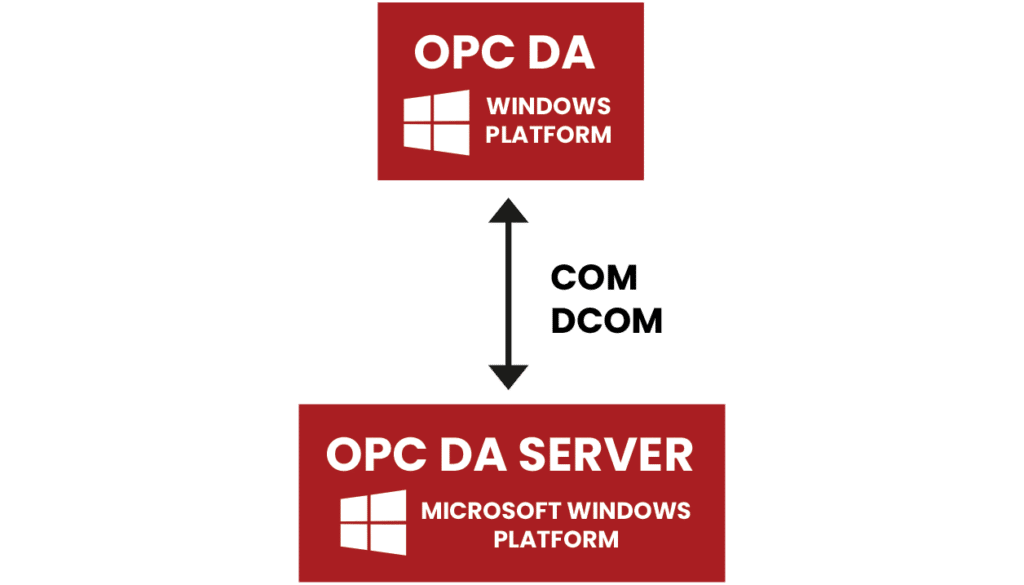
Microsoft systems with COM/DCOM protocol.
Data Access
OPC DA transmits real-time values from PLCs to HMI/SCADA systems, transferring information about Item (tag name), Value, Time (timestamp for when the value was read), and Quality (data validity).
Alarm & Events
OPC A&E only sends information about Time, describing when the event or alarm was read with a timestamp. Additionally, OPC A&E transmits the information without storing anything.
Historical Data Access
OPC HDA contains historical data that you can query and supports the transfer of large amounts of data from one or more tags. It was actually created to provide a comprehensive way to retrieve data from process databases. The protocol is not widely used today.
XLM/CSV
OPC XML makes process data available on any operating system that uses XML. OPC CSV allows OPC data to be stored as CSV files, which can then be read in spreadsheet systems like Excel.
Data Exchange
OPC DX provides a standardized method for transferring data between different OPC servers and other devices such as PLCs, HMI/SCADA systems, and PCs.
The latest standard: OPC UA
When more operating systems gained popularity, the need for a platform-independent OPC solution arose. In 2006, the OPC Foundation launched OPC UA – Unified Architecture. Unlike the classical standards, it does not rely on Microsoft technology, and the server can run on Apple, Linux, and Windows. Network communication is simplified.
Additionally, OPC providers desired a single platform with access to all OPC models. OPC UA comes with features for utilizing structures and models, allowing tags to be grouped and managed as a unit.
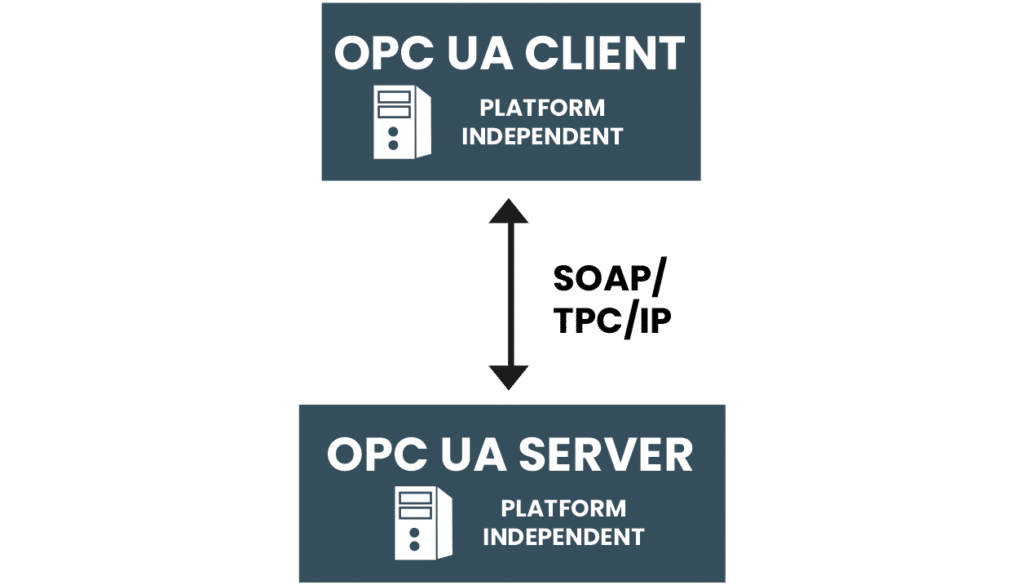
platforms with SOAP or TCP/IP protocols.
Information Modeling
OPC UA features functions that allow you to utilize structures and models. These models can be defined by vendors or protocols. The servers can also contain structures with more complex relationships between tags and nodes. This functionality enables the creation of data structures where certain data is always grouped and handled as a unit. This proves useful when you aim to ensure that datasets are retrieved simultaneously.
Communication
Communication is structured with layers built atop the standard TCP/IP transport layer. Above this layer, two layers maintain and manage a secure channel between the server and client, relying on SSL, HTTP, or HTTPS. This communication layer secures the entire channel, safeguarding against any potential data corruption. Additionally, X.509 certificates can be exchanged between the server and client for added security.
OPC UA is primarily used to bridge different OPC DA servers, a process known as “tunneling.” This enables network-based communication to be achieved.
Should you choose classical OPC or OPC UA?
Many industrial companies still use classical OPC standards for industrial communication. These systems are often implemented before OPC UA became available, or they have older systems/equipment that cannot communicate with OPC UA. As long as the system functions properly, this is not a problem.
For new OPC implementations, OPC UA is a natural choice. It offers the same functionalities as classical OPC standards, provides connectivity to multiple operating systems, and offers better security.
Take a look at KEPserverEX from Kepware for OPC communication.